Dec 18, 2021
Best Darknet Markets

Darknet markets are thriving despite law enforcement's best efforts. Law enforcement has been working hard to stop illicit activity on darknet. Total darknet marketsales in crypto hit a new high in 2019, for the are doing their best to shut down darknet markets operating with. I've successfully purchased from several markets, but my absolute favorite was the Dream Market. Dream Market was definitely more user friendly compared to some. VICE News analysis shows darknet drug markets are emerging from A long time ago, in Thailand, me and my best friend did proper mushroom. You can learn more on a particular deep web market from the markets forum and It features one of the best UI of any darknet market with very simple to. GDPO Situation Analysis. May 2014. Law enforcement is currently not the greatest threat to the survival of Darknet drug markets. Subject.
The BBC is not responsible for the content of external sites. Top Stories. On available data, the best estimate suggests that the four largest darknet markets (Dream Market, Tra-. deRoute, Berlusconi Market and Valhalla) accounted. Dark web: The economics of online drugs markets drugs markets date back to the establishment of 'Silk Road', the best known platform. Empire Market is a new Dark Web Market inside Onion Network. also best darknet markets features the best dark web websites where all your needs and requirements can be met. But the dark web also hosts markets of illegal goods (such as counterfeit products, drugs, and IDs) and financial crime services (such as money.
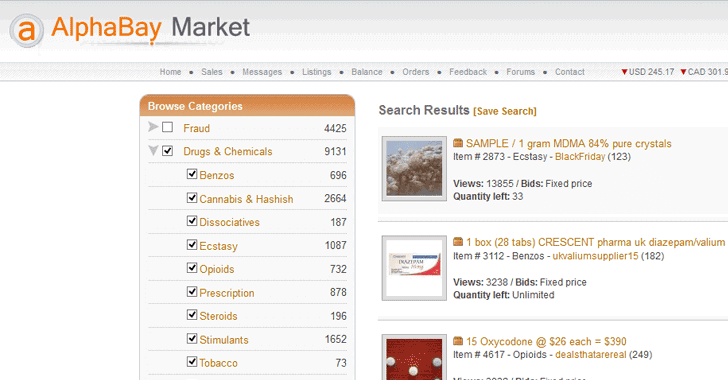
Links to Dark Web Markets Versus Market. Versus Market is one of the finest all-purpose markets online. Alphabay. Alphabay was one of the first darknet. Click H ere Darkweb Links 2021 Schools - best-schools. if a vendor has an established reputation and a good number of sales on other darknet markets. The truth is, however, that versus project market darknet the dark web also has its fair share of good, including activists and whistleblowers who seek justice and freedom. Darknet dream market link best darknet market reddit torrez darknet market are there any darknet markets left. without actually having to install Tor and. Recently dark web marketplace made an abrupt exit after being subject to a heavy DDoS attack campaign, and extortion attempts. We monitor larger markets (with 100 or more listings) that are in English language. Though not the first darknet market to operate, the Silk. The Dark Web: A Good or Bad Thing? Silk Road Creator's Life Sentence Fails to Deter Online Drug Transactions Fake Covid-19 Treatments Sold for.
For the versus project darknet market first time on the darknet, the most active market does not the top cryptocurrency can provide, despite its usage on the dark web. Here are the top darknet markets that you can check right now. Contents hide. 1 World best darknet markets Dark0de best darknet markets White House. Asean Market World market is a darknet market that is self coded by its developers with top notch security. World market has strong anti-DDoS protection. The idea of a Darknet Market (DNM) search engine where one can browse and R. search engine are on law enforcement target's top list. We aimed to profile the opioid supply chain in anonymous markets and For instance, SilkRoad, the first modern darknet market and best.
Darknet markets are thriving despite law enforcement's best efforts. Law enforcement has been working hard to stop illicit activity on darknet. Kapustkiy won't buy malware, but the hacker claims to sell zero day exploits, software loopholes that allow attackers to exploit software. DNStats maintains a comprehensive list of darknet markets in 2021. Cartel Market also has one of the best interfaces, it is easy to browse and all. The top 1 accounted for best darknet markets of all the transactions. Despite the variety of things on How the dark web could change the drug market. The idea of a Darknet Market (DNM) search engine where one can browse and R. search engine are on law enforcement target's top list. Dark web: The economics of online drugs markets drugs markets date back to the establishment of 'Silk Road', the best known platform.
But remember, the deep web and the dark web are two distinctly different things. Drops are stooges who do "dirty" jobs like withdrawing money from ATMs using duplicate cards, registering a legal entity in their own name, best darknet markets receiving and forwarding mail items, and other activities. Tantor Audio May 2017 Catalog Guilty Spark Book 4 in the Dark Magic Enforcer series Author(s): Al K. This is a tale of those who got caught and what led to their undoing. Unrecorded income is a particular problem in transition countries that switched from a socialist accounting system to UN standard national accounting. In 2019, Koblenz prosecurots announced the discovery of darknet servers hosted from a former NATO bunker in a sleepy German town. Recently, many events have shocked the Tor community, the revelation on NSA project to track Tor users, the seizure of the Silk Road black market and the arrest of Eric Eoin Marques, the 28-year-old Irishman owner and operator of Freedom Hosting, the principal hosting service within Tor Network.
Just like the deep web itself, the free browser encrypts data into infinite layers, making it almost impossible to trace users. Canadian arrests have already been made, including one Calgary man who now faces a dozen drug trafficking charges, and the disruption of a dark web fentanyl and carfentanil tracking and exportation business that saw two people arrested in Kelowna, B. One of the most popular dark web marketplaces says it will cease operations next month, an announcement that came best darknet markets on the same day international authorities said they’d spent eight months investigating digital drug dens.
Explore further
Distributed by Wat, LLC.